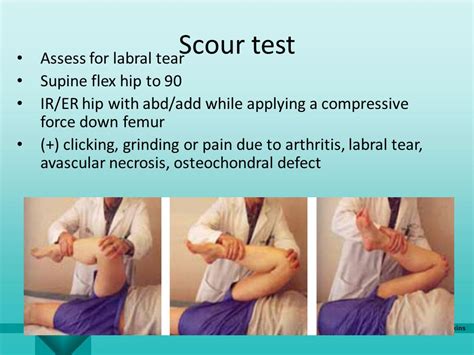
anterior labral tear fitzgerald test|fitzgerald labrum : wholesaling Fitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. Patrick test - For assessment of the posterior labrum. The patient's hip is flexed and then extended while in .
Follow he manufacturer's instructions for loading the autoclave. This will help ensure that you are using the autoclave correctly and safely. Please don't go off of what you .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Autoclave, vessel, usually of steel, able to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The chemical industry uses various types of autoclaves in manufacturing dyes and in other chemical reactions requiring .
The Fitzgerald test utilises two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. See more
Anterior labrum The patient lies supine while the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by hip . See more
The Fitzgerald test has been shown to have a sensitivity of between 0.98 and 1.00. The specificity is unknown. See moreFitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. Patrick test - For assessment of .The Fitzgerald test utilises two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. Technique. Anterior labrum. The patient lies supine while the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by hip extension, internal rotation, and adduction [1] [2].Fitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. Patrick test - For assessment of the posterior labrum. The patient's hip is flexed and then extended while in .
positive labral tear test
Fitzgerald's Test. Purpose: To assess for a labral tear. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: To assess for anterior labral tears: the affected limb is placed in full flexion, lateral rotation, and abduction. The examiner then extends the hip passively, while moving it through medial rotation, and adduction as well.
The clinician takes the hip into full flexion, external rotation, and full abduction as a starting position.Describe anatomical and physiological characteristics of the acetabular labrum predisposing it to injury. Outline risk factors contributing to the development of acetabular labral tears. Identify common biomechanical/musculoskeletal deficiencies in patients with acetabular labral tears.
There are a number of clinical tests and subjective pieces of information that clinicians may associate with labral pathology of the hip. Fortunately Burgress and crew (2011) have performed a systematic review to identify the diagnostic accuracy of these clinical tests.The Fitzgerald test utilizes two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. To test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by extending the hip, internal rotation, and .
labral tear test results
The most consistent physical exam finding in patients with acetabular labral tears is a positive anterior hip-impingement test [13, 35, 92]. This is performed with the patient supine with the hip and knee at 90° of flexion.
The content is intended as educational content for health care professionals and students. If you are a patient, seek care of a health care professional. In this short video, Kai demonstrates how to assess for an anterior labral tear.Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.The Fitzgerald test utilises two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. Technique. Anterior labrum. The patient lies supine while the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by hip extension, internal rotation, and adduction [1] [2].Fitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. Patrick test - For assessment of the posterior labrum. The patient's hip is flexed and then extended while in .
labral tear differential diagnosis
Fitzgerald's Test. Purpose: To assess for a labral tear. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: To assess for anterior labral tears: the affected limb is placed in full flexion, lateral rotation, and abduction. The examiner then extends the hip passively, while moving it through medial rotation, and adduction as well.The clinician takes the hip into full flexion, external rotation, and full abduction as a starting position.
Describe anatomical and physiological characteristics of the acetabular labrum predisposing it to injury. Outline risk factors contributing to the development of acetabular labral tears. Identify common biomechanical/musculoskeletal deficiencies in patients with acetabular labral tears. There are a number of clinical tests and subjective pieces of information that clinicians may associate with labral pathology of the hip. Fortunately Burgress and crew (2011) have performed a systematic review to identify the diagnostic accuracy of these clinical tests.
The Fitzgerald test utilizes two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. To test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by extending the hip, internal rotation, and .
The most consistent physical exam finding in patients with acetabular labral tears is a positive anterior hip-impingement test [13, 35, 92]. This is performed with the patient supine with the hip and knee at 90° of flexion. The content is intended as educational content for health care professionals and students. If you are a patient, seek care of a health care professional. In this short video, Kai demonstrates how to assess for an anterior labral tear.

fitzgerald labrum test
fitzgerald labrum
anterior posterior labral tear
An autoclave is a machine that uses steam under pressure to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores on items that are placed inside a pressure vessel. The items are heated to an .
anterior labral tear fitzgerald test|fitzgerald labrum